Advertisement
When working with lists in Python, changing values often shows up. Maybe you need to swap a number, update certain words, or clean up a batch of data. Fortunately, Python offers several ways to get this done—some are simple and direct, while others give you more control or flexibility depending on what you're trying to replace.
This article will walk you through all the possible ways you can replace values in a list in Python, with examples that help make sense of when and how to use them.
The most straightforward way to replace a value is by accessing its position in the list. Python lists are indexed, so if you know the position of the item you want to change, it’s just a matter of assignment.
python
CopyEdit
my_list = [10, 20, 30, 40]
my_list[2] = 99
print(my_list) # [10, 20, 99, 40]
This only works when you know the index. It doesn’t help if you’re trying to replace a value without knowing where it is in the list.

When you want to replace a value based on what it is (not where it is), a simple loop does the job. It checks each item and changes it if it matches what you're looking for.
python
CopyEdit
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 2, 4]
for i in range(len(my_list)):
if my_list[i] == 2:
my_list[i] = 99
print(my_list) # [1, 99, 3, 99, 4]
This is useful when the value appears more than once or its position isn’t fixed. You get full control over which values to replace.
If you're familiar with list comprehensions, you can use them to build a new list with the desired values. It’s a clean one-liner that works well for simple conditions.
python
CopyEdit
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 2, 4]
new_list = [99 if x == 2 else x for x in my_list]
print(new_list) # [1, 99, 3, 99, 4]
This won’t change the original list unless you assign it back to the same name. It’s more Pythonic, though, and often preferred for its clarity.
The map() function lets you apply a function to each item. You can combine it with a lambda if you want a compact way to conditionally replace values.
python
CopyEdit
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 2, 4]
new_list = list(map(lambda x: 99 if x == 2 else x, my_list))
print(new_list) # [1, 99, 3, 99, 4]
This is very similar to list comprehension in behavior but may feel cleaner in some functional programming patterns.
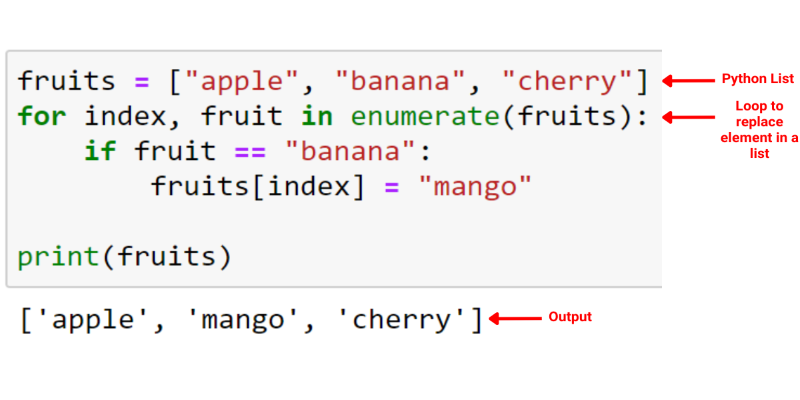
If you need both the index and the value while looping, enumerate() is a practical option. It's helpful when you want to update the list.
python
CopyEdit
my_list = [5, 6, 7, 6]
for idx, val in enumerate(my_list):
if val == 6:
my_list[idx] = 0
print(my_list) # [5, 0, 7, 0]
This gives a clear structure when you’re working with indexes, and it avoids the need to manage a separate index counter.
If your list has strings and you want to update part of the string (not the whole item), you can use replace() inside a comprehension.
python
CopyEdit
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'apricot']
new_list = [x.replace('ap', 'xy') for x in my_list]
print(new_list) # ['xyple', 'banana', 'xyricot']
This is useful when you’re not replacing whole items but modifying parts of the contents.
For lists where the same item shows up more than once, and you want to replace all of them without using a loop that checks each element, you can use a while loop along with index().
python
CopyEdit
my_list = [3, 4, 3, 5, 3]
while 3 in my_list:
idx = my_list.index(3)
my_list[idx] = 0
print(my_list) # [0, 4, 0, 5, 0]
This works well, but it isn't the fastest method for large lists. Still, it's handy if you want to replace by value and skip writing out a loop.
If you’re dealing with numerical data and already using NumPy, replacing values becomes even easier. NumPy lets you replace values conditionally with simple expressions.
python
CopyEdit
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 2, 4])
arr[arr == 2] = 99
print(arr) # [ 1 99 3 99 4]
It doesn’t work on regular Python lists, but if you're processing arrays, this method is fast and expressive.
If you're working with data in pandas.Series, the replace() method offers a direct way to update values.
python
CopyEdit
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 2])
s = s.replace(2, 99)
print(s.tolist()) # [1, 99, 3, 99]
This is common in data analysis tasks where you have structured columns and want a simple way to substitute one value for another.
If you want to replace a portion of a list at known positions, slicing is quick and avoids loops altogether.
python
CopyEdit
my_list = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
my_list[1:4] = [0, 0, 0]
print(my_list) # [10, 0, 0, 0, 50]
Just be sure the replacement segment has the same number of items, or the list's length will be changed.
Python doesn’t limit you to one method for updating list values. Whether you’re working with indexes, conditions, ranges, or external libraries like NumPy or pandas, there’s always a way that fits your task. The choice depends on whether you want clarity, speed, or flexibility. Knowing your options makes it easy to pick the right one without overcomplicating the code.
Advertisement

Explore how Rabbit R1 enhances enterprise productivity with AI-powered features that streamline and optimize workflows.

Salesforce brings generative AI to the Financial Services Cloud, transforming banking with smarter automation and client insights

Discover different methods to check if an element exists in a list in Python. From simple techniques like using in to more advanced methods like binary search, explore all the ways to efficiently check membership in a Python list

Discover top industries for AI contact centers—healthcare, banking fraud detection, retail, and a few others.
Learn how to loop through dictionaries in Python with clean examples. Covers keys, values, items, sorted order, nesting, and more for efficient iteration

Think generative AI risks are under control? Learn why security issues tied to AI models are growing fast—and why current defenses might not be enough

Master the Python list insert() method with this easy-to-follow guide. Learn how to insert element in list at specific positions using simple examples

Learn how the Python list extend() method works with practical, easy-to-follow examples. Understand how it differs from append and when to use each

Learn 10 clean and effective ways to iterate over a list in Python. From simple loops to advanced tools like zip, map, and deque, this guide shows you all the options

Explore how the New York Times vs OpenAI lawsuit could reshape media rights, copyright laws, and AI-generated content.
Want to organize your pandas DataFrame without confusion? This guide shows clear, practical ways to sort by values, index, custom logic, or within groups

Understand deepfakes, their impact, the creation process, and simple tips to identify and avoid falling for fake media.