Advertisement
Advertisers are always looking for technologies that can provide them with a creative and performance-driven advantage as the terrain of digital marketing changes at a dizzying speed. Emerging as a transforming agent in this field, artificial intelligence (AI) is simplifying creative processes, optimising ad targeting, and enabling mass personalised experiences. Amazon has boldly shown its dedication to innovation by launching AI-powered picture-generating tools to allow marketers to produce more interesting, customised, and powerful visual content.

Visuals typically provide the first—and perhaps only—impression a brand makes on prospective consumers in the very competitive realm of Internet commerce. Studies reveal that viewers of visually appealing material are more likely to interact with, remember, and act upon. Image quality and relevancy strongly affect click-through rates and purchase choices on e-commerce sites such as Amazon, where hundreds of like goods vie for attention.
However, keeping a pipeline of excellent, contextually suitable photos is difficult, particularly for small to medium-sized companies (SMBs). Hiring photographers, leasing venues, and running photo sessions all need resources. Thanks to Amazon's AI picture tools, companies can now quickly create images that satisfy technical requirements and emotionally connect with target markets, negating many of these restrictions.
Fundamentally, Amazon's AI toolkit consists of a powerful generative artificial intelligence engine taught on vast consumer interaction patterns, lifestyle situations, and product imagery databases. Standard product images—often on white backgrounds—can be uploaded by marketers using technology and transformed into rich, contextual settings that position the product within a lifestyle environment. Models like those utilised in picture synthesis tools like DALL-E and Stable Diffusion but customised especially for trade drive this metamorphosis.
Advertisers choose characteristics like the product kind, preferred scenario setting (e.g., kitchen, workplace, outdoor patio), lighting conditions, and optional seasonal or demographic indications via the simple user interface. After that, artificial intelligence creates a range of picture choices, including the product, in the chosen setting. These outputs fit for usage across Amazon's native ad formats and are realistic and brand-consistent; testing many versions helps one find which visual appeals most to a certain target group.
Amazon's AI picture-generating technologies have far-reaching pragmatic benefits. They first cut out one of the most time-consuming tasks in the advertising process—visual asset generation. Advertisers may create a tailored picture portfolio in minutes with only a few inputs, facilitating speedier campaign starts and more agile iteration. This is especially helpful during holidays like Prime Day when timing and relevancy are critical.
Second, the tools improve scalability and personalising capabilities. Marketers may change backgrounds, settings, and themes depending on consumer personalities, areas, and browsing behaviour, creating many visual storylines for various audience groups. Only major companies with vast creative teams could access this detail in visual materials. Now, SMBs can compete on equal footing, using AI to reach customers where they are—with images that directly speak to their lifestyles and objectives.
The way Amazon's AI picture technologies fit the larger Amazon advertising platform is one of its best qualities. These tools are part of the campaign management processes of Amazon Ads, not separate design tools. This guarantees that the produced images are best suited for many ad places, including Amazon DSP display advertisements, Sponsored Brands, and Sponsored Products.
The connection lets marketers see, in real time, how each picture would seem within Amazon's layout templates. Furthermore, Amazon's back-end algorithms may examine engagement indicators—such as conversion rates and impression-to-click ratios—to suggest iterative picture-producing process improvements. This data-driven feedback loop improves ad effectiveness and clarifies for marketers which graphic components best fit their target market.
These tools provide promise, but their use is not without difficulty. A worry is the possibility of creative homogeneity. Should numerous companies depend on identical artificial intelligence algorithms to create pictures, graphics across brands risk becoming formulaic or too polished, therefore losing the distinctiveness that usually creates brand loyalty and emotional connection.
Important factors also include ethics and openness. Should companies reveal if the graphics used in their ads are created by artificial intelligence? AI may improve realism, but there's a thin line between aspirational and deceptive. Eventually, regulators and advertising standards boards might have to intervene, especially if consumer concerns about dishonesty or misrepresentation result from AI-generated images.
Introducing artificial intelligence technologies into the creative process naturally begs issues about the direction of creative professions. The truth is more complex than some might worry—that artificial intelligence will replace content creators, graphic designers, and photographers, among other occupations. These instruments are more likely to inspire human ingenuity than to replace it.
AI technologies allow designers, for example, to prototype ideas quicker, investigate a greater range of visual possibilities, and concentrate their efforts on narrative and campaign strategy. By handling ordinary or repetitive activities, artificial intelligence releases the human ability for high-level creative judgements. Teams that carefully use artificial intelligence in their processes may see higher production, quicker innovation, and more consistent branding across all media.
Amazon's introduction of AI-driven creative tools points to a more general trend transforming the advertising and marketing sectors. The creative pipeline will become more automated and data-driven as artificial intelligence gets more skilled at producing photos and video, audio, and textual materials. Companies can react to real-time trends, creating customised micro-segment materials at unthinkable volumes.
Additionally, more immersive and interactive advertising will be the direction of advertising in the future. AI-generated 3D product representations, virtual try-ons, and augmented reality experiences all stemming from a basic product photograph might not be far off. With its technology setup and large market, Amazon is positioned to spearhead this change and enable marketers to transform basic product displays into dynamic, emotionally powerful events.

Amazon's artificial intelligence picture-generating tools represent a major development in the conception, production, and use of digital advertising. Amazon is democratising access to sophisticated creative skills reserved for elite marketing teams by arming marketers to create high-quality, relevant images at scale. These technologies allow quick content creation, customised narrative, and performance optimisation inside a single platform.
However, mastery of AI-generated images calls for much more than technological acceptance. Advertisers have to carefully strike a mix between authenticity and efficiency so that their pictures complement customer expectations and brand values. They also have to be alert regarding the moral application of artificial intelligence, especially given the blurring of real and synthetic content borders. When utilized sensibly, Amazon's AI picture tools provide a potent method of releasing creativity, increasing interaction, and hastening expansion in the always-changing digital marketplace.
Advertisement

Learn how the Python list extend() method works with practical, easy-to-follow examples. Understand how it differs from append and when to use each

Master the Python list insert() method with this easy-to-follow guide. Learn how to insert element in list at specific positions using simple examples

Explore how developers utilize the OpenAI GPT Store to build, share, and showcase their powerful custom GPT-based apps.
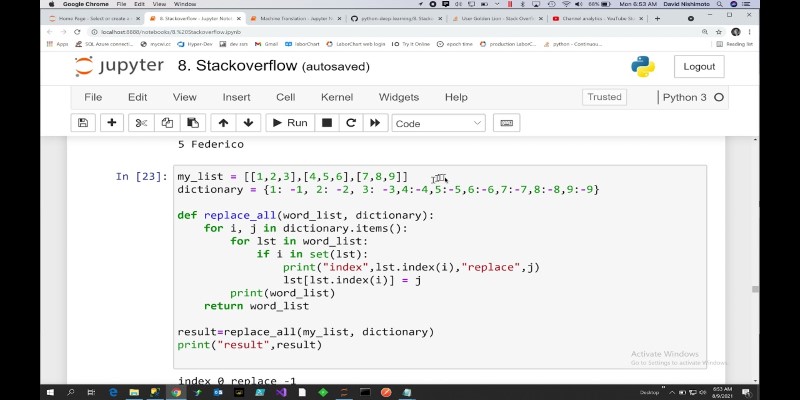
How to replace values in a list in Python with 10 easy methods. From simple index assignment to advanced list comprehension, explore the most effective ways to modify your Python lists

Explore how Rabbit R1 enhances enterprise productivity with AI-powered features that streamline and optimize workflows.

Understand deepfakes, their impact, the creation process, and simple tips to identify and avoid falling for fake media.

Discover Oracle’s GenAI: built-in LLMs, data privacy guarantees, seamless Fusion Cloud integration, and more.

Need to share a ChatGPT chat? Whether it’s for work, fun, or team use, here are 7 simple ways to copy, link, or export your conversation clearly
Need to save your pandas DataFrame as a CSV file but not sure which method fits best? Here are all the practical ways to do it—simple, flexible, and code-ready

Explore how the New York Times vs OpenAI lawsuit could reshape media rights, copyright laws, and AI-generated content.

Learn how __init__ in Python works to initialize objects during class creation. This guide explains how the Python class constructor sets instance variables, handles defaults, and simplifies object setup
Learn how to loop through dictionaries in Python with clean examples. Covers keys, values, items, sorted order, nesting, and more for efficient iteration